The Brain Needs Animal Fat
I try very hard to restrict my protein intake to grass fed pastured animals, birds, and wild caught fish. This article discusses the value of the associated fats, and why these fats are good for a healthy body and specifically the brain.
Why humans can’t thrive on plants alone.
Author: Georgia Ede MD
Posted Mar 31, 2019
Source: nexusplexus / 123RF Stock Photo
When you think of animal fat, what comes to mind? Unsightly blobs of cellulite? Artery-clogging strips of gristle to be trimmed off your steak and tossed into the trash? Or a sophisticated substance that contains within it the secret to human intelligence?
Fun facts about fat
We think of fat as bad—the less of it we eat, and the less of it we carry on our bodies, the better—but this isn’t the right way to think about it. Fat is not just for insulation and energy storage, it’s also for nutrient absorption, cell signaling, immune function, and many other critical processes. Many people think the main difference between plant and animal fats is that animal-sourced foods contain more saturated fat, but here are a few fun, fatty facts that may surprise you:
1. All whole plant and animal foods naturally contain a mixture of saturated and unsaturated fats.
2. Some plant foods are higher in saturated fat than animal foods, with coconut oil topping the charts at 90 percent saturated fat. That’s more than twice the saturated fat found in beef fat (tallow).
3. The primary type of fat found in pork is a monounsaturated fatty acid (MUFA) called oleic acid, the same fat found in olive oil.
For decades now, we’ve been told to avoid saturated fats—particularly those from animal foods—and to consume “heart-healthy,” cholesterol-free fats from plant foods, such as seeds, nuts, and olives. Public health officials say these magical plant fats are rich in important PUFAs (polyunsaturated fatty acids) that the human body cannot manufacture and therefore must be obtained from the diet:
- The essential dietary omega-3 is called Alpha-Linolenic Acid (ALA for short).
- The essential dietary omega-6 is called Linoleic Acid (LA for short).
What often goes unsaid is that both ALA and LA are found in a wide variety of both plant and animal foods, so it is rather easy to obtain both of these PUFAs, regardless of your dietary preferences, so long as you are including enough fat in your diet.
But here’s the rub: Our bodies really aren’t looking for ALA and LA; they’re looking for something better. ALA and LA are considered “parent” omegas, because they are used to manufacture the omegas we actually need: EPA, DHA, and ARA—none of which exist in plant foods.
EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) is an omega-3 that serves primarily anti-inflammatory and healing functions.
ARA (arachidonic acid) is an omega-6 often thought of as a “bad” fatty acid, because it promotes inflammation. But ARA shoulders countless other responsibilities, and even promotes healing. [This intriguing, beneficial, and much-misunderstood molecule recently stepped into my office for a long-overdue therapy session. You can read a transcript of our conversation here.]
And what about DHA? So glad you asked…
Introducing DHA
Our brains are extremely rich in fat. About two-thirds of the human brain is fat, and a full 20 percent of that fat is a very special essential omega-3 fatty acid called docosahexanoic acid, or DHA.
DHA is an ancient molecule so useful to us and our fellow vertebrates (creatures with backbones) that it has remained unchanged for more than 500 million years of evolution. What makes this particular PUFA so irreplaceable?
DHA’s job description is a lengthy one. Among many other functions, DHA participates in the formation of myelin, the white matter that insulates our brain circuits. It also helps maintain the integrity of the blood-brain barrier, which keeps the brain safe from unwanted outside influences.
Perhaps most importantly, DHA is critical to the development of the human cortex—the part of the brain responsible for higher-order thinking. Without DHA, the highly sophisticated connections necessary for sustained attention, decision-making, and complex problem-solving do not form properly. It has been hypothesized that without DHA, consciousness and symbolic thinking—hallmarks of the human race—would be impossible.
DHA plays a “unique and indispensable role” in the “neural signaling essential for higher intelligence.” —Simon Dyall PhD, Lipid Research Scientist Bournemouth University, UK
Professor Michael Crawford, a pioneering British scientist who has been studying essential fatty acids for 50 years, theorizes that DHA’s special configuration lends it unique quantum mechanical properties that allow it to buffer electron flow. This may explain why we find it in places throughout the brain and body where electricity is important: synapses where brain cell signaling takes place; mitochondria, where the electron transport chain is busy turning food into stored energy; and the retina of the eye, where photons of sunlight are transformed into electrical information.
This is a truly miraculous molecule. Plants don’t have it, because plants don’t need it.
Baby, have we got a molecule for you…
The most rapid phase of development of the infant cortex takes place between the beginning of the third trimester of pregnancy and age 2. If enough DHA isn’t available to the baby during this critical 27-month window, it is unclear whether the consequences can be completely undone. In fact we do see lower levels of DHA in people diagnosed with psychiatric disorders, including those which manifest early in life, such as autistic spectrum disorders and ADHD.
“Similar to children and adolescents born preterm, patients with ADHD, mood disorders, and psychotic disorders also exhibit decreased frontal white matter tract integrity and reduced functional connectivity within cortical networks. Together these findings support the hypothesis that perinatal deficits in DHA accrual may contribute to diminished cortical circuit development observed in major psychiatric disorders” (McNamara RK 2015).
Plant foods contain absolutely no DHA
For those who choose vegan diets, it is important to know that plant foods contain no DHA. The omega-3 fatty acid found in plant foods like flax, walnut, and chia is alpha-linolenic acid (ALA). Unfortunately, it appears to be rather difficult for the adult human body to make DHA out of ALA, with most studies finding a conversion rate of less than 10 percent:
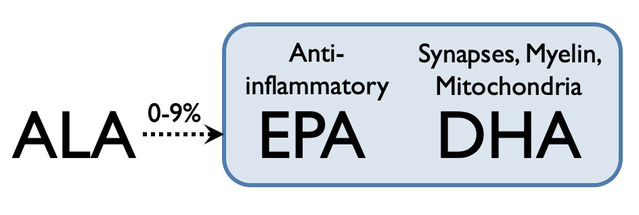
Note that quite a few studies find a conversion rate of 0 percent.
Whether this pathway can generate adequate amounts of DHA in all adults under all circumstances continues to be a topic of debate. Some scientists have advocated that DHA, rather than ALA, should be officially considered the essential omega-3 fatty acid. Even vocal advocates of plant-based diets, such as the authors of the recent EAT-Lancet report, acknowledge that it is unclear how much ALA one needs to consume to fulfill DHA requirements.
Indeed, it appears that the fewer animal foods we eat, the lower our DHA levels tend to be:

However, when it comes to children younger than 2 years old, the science is clear that this conversion pathway cannot and should not be relied upon to keep pace with the DHA demands of the rapidly growing body and brain. Therefore, most experts agree that caretakers should provide infants and very young children with dietary or supplemental sources of DHA, as ALA alone is not sufficient to support healthy infant development.
DHA status and intake recommendations are based on blood levels, not brain levels. Unfortunately there is no way to measure brain DHA levels in living human beings, and it’s unclear whether blood levels reflect brain levels.
Bearing this in mind, it has been estimated that as many as 80 percent of Americans have suboptimal blood levels of DHA.
DHA: Don’t leave home without it
Include animal-sourced foods in your diet if you can
The USDA has not established specific DHA intake targets for the general population; instead it recommends everyone consume at least eight ounces of seafood per week. The easiest way to obtain DHA is to include some fatty fish in your diet, but as you can see from the table below, there are other options.
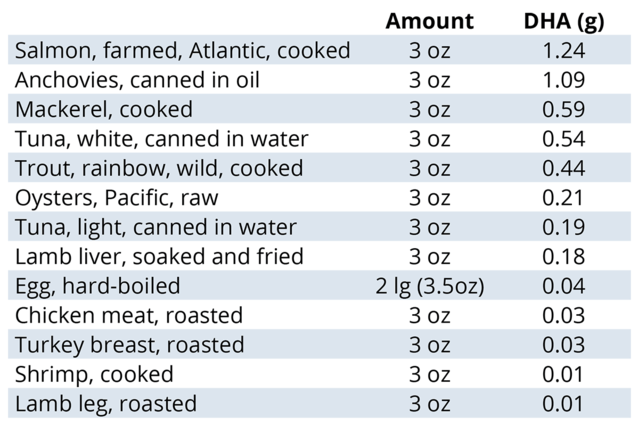
Source: Data from USDA National Nutrient Database 2016.
Minimize consumption of vegetable oils
Nearly all processed foods, prepared hot foods, packaged snacks, and convenience foods are made with refined vegetable oils, such as soybean or sunflower oil. Most vegetable oils are extremely, unnaturally high in LA (linoleic acid), an omega-6 fatty acid that reduces the production and effectiveness of DHA within your body. Excess linoleic acid can tilt your immune system too far towards inflammation and away from healing, so there are many reasons to minimize your consumption of vegetable oils. Your best plant oil choices are olive oil, avocado oil, coconut oil, or red palm oil. If you must include refined vegetable oil, canola oil and palm kernel oil are low in linoleic acid. Lowering your vegetable oil intake can increase the availability of DHA in your body, decreasing your need for dietary and/or supplemental DHA. The presence of high amounts of linoleic acid in the typical modern diet may help to explain why so many people appear to have low DHA levels despite the fact that most people do include animal foods in their diet already.
If you choose a plant-based diet, supplement properly
Thankfully, vegetarian and vegan-friendly DHA supplements extracted from algae are available. [Algae are neither plants nor animals . . . discuss!] These supplements are more expensive and contain lower concentrations of DHA than fish or krill oil supplements (meaning higher doses are recommended), but may be important for maintaining healthy DHA levels, particularly in mothers and babies during pregnancy and while breastfeeding. Directly consuming seaweed and other forms of edible algae instead of taking algae oil extracts is unreliable, because it’s unclear whether the DHA within these fibrous foods can be released and absorbed by the human body; in other words, the DHA in edible algae may not be bioavailable. All baby formula in the U.S. is supplemented with DHA already, in an effort to mirror human mother’s milk, which naturally contains DHA. If weaning your child before age 2, be sure to include DHA in your child’s diet as food or supplements.
If you have psychiatric symptoms, consider supplementation
There have been numerous clinical trials of omega-3 supplements in the management of psychiatric disorders. You may be surprised to hear that most of these studies have generated only weak or mixed results. There are many possible reasons for this, not the least of which may be that the amount of linoleic acid in the diet was not taken into consideration. In other words, taking a decent dose of omega-3s without also lowering your linoleic acid consumption (by avoiding vegetable oils) may not be very helpful. However, supplementation is widely viewed as safe, and some studies noted modest benefits at doses of (combined EPA+DHA) of 1,000 to 2,000 mg per day, particularly for people with depression.
Unanswered questions
I titled this post “The Brain Needs Animal Fat,” because although DHA does exist in algae, algae are not plants, and we don’t know if we can access the DHA within edible algae without special extraction methods. Prior to the availability of algae-derived supplements (which only became available recently), the only pre-formed DHA naturally bioavailable to everyone would have come from animal foods. For those who choose a vegan diet, I fully support and recommend algae-based supplements.
It is difficult to be sure precisely how much DHA we need, and both conversion rates and availability can vary significantly depending on age, gender, genetics, and dietary composition.
There are many questions left unanswered that go beyond the scope of this post and may deserve a follow-up post. For example, if most land animals are extremely low in DHA, does that mean everyone needs to eat seafood? Are wild land animal foods higher in DHA than standard land animal foods we find in the grocery store? How do adults choosing plant-based diets know whether they can rely on their ALA conversion pathway? Could eliminating processed foods and vegetable oils completely eliminate the apparent requirement for animal-sourced DHA (or algae oil supplementation)? Does eating a low-carbohydrate diet affect the conversion rate from ALA to DHA? Should you get tested for omega-3 deficiencies, and if so, how? Are there any disadvantages to obtaining DHA from supplements as opposed to obtaining them from animal foods?
The bottom line about DHA
Until next time, minimizing refined vegetable oils and other processed foods, and either including some animal foods in the diet or supplementing appropriately, seem to be reasonable options that likely minimize our risk.
One thing is clear. DHA is a wondrous fatty acid that the human body cannot function without, and it deserves our admiration and respect. While it is important for all of us, when it comes to building the brains of the future, it is precious and irreplaceable.
Learn More about the author: Georgia Ede MD
Facebook Image Credit: Rido/Shutterstock





Recent Comments